How Businesses Can Reduce Their Fossil Fuel Dependency

With time to achieve global climate goals running out, moving away from fossil fuels becomes more important than ever.
Nevertheless, both the global economy and business processes still heavily depend on these energy sources.
From gasoline used to run corporate fleets and planes, to natural gas heating offices, it is hard to imagine a world without fossil fuels.
This article summarises why and how we can foster the green transition.
Why do businesses need to transition away from fossil fuels?
Fossil fuels are all those non-renewable energy sources that currently provide 80% of the world’s energy (Our World In Data, n.d.).
They include coal, crude oil, and natural gas. The name derives from the fossilisation of organic materials, which are then extracted and burned to generate energy.
We started burning fossil fuels during the Industrial Revolution, and since then we’ve been heavily reliant on them.
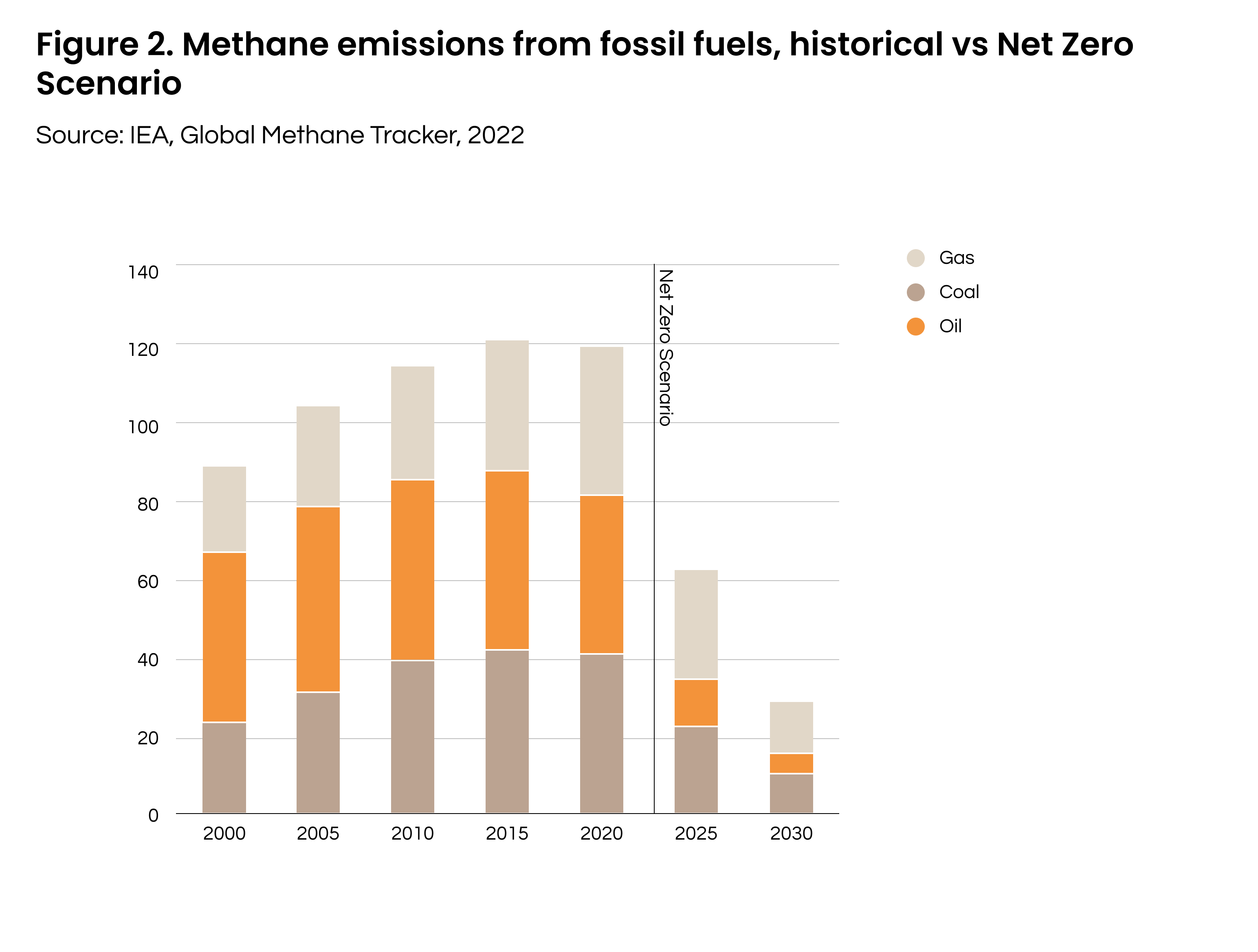
Figure 1 represents the global fossil fuel consumption per type. As shown below, our use of these sources has grown over time.
Nevertheless, we need to move away from them and fast.
The IPCC states that emissions from fossil fuels are the main cause of global warming. With over 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions coming from fossil fuels, the link between global warming and non-renewables is evident (UN, n.d.).
More specifically, Inside Climate News (2019) highlights that:
- Coal is responsible for more than 0.3°C of the 1°C increase in global average temperatures;
- Oil accounts for 1/3 of the world’s total carbon emissions;
- Natural Gas is responsible for at least 1/5 of the world’s total carbon emissions.
To stay within the path set out by the Paris Agreement in 2015, the IPCC stresses the need to halve fossil fuel emissions within 11 years.
Despite these figures, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) estimates that by 2030 we will produce more than double the amount of coal, oil and gas we can burn to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
The cost(s) of burning fossil fuels
Burning fossil fuels does come at a cost(s).
Aside from fossil fuel prices rising rapidly, environmental and social costs are significant too.
Emissions and Global Warming Pollution
As stated above, fossil fuels are amongst the biggest contributors to global temperatures increase.
Aside from releasing huge quantities of CO2 when burned, fossil fuels also emit other toxic air pollutants that jeopardise human health.
Land Degradation
The extraction, treatment and transportation of oil, gas and coal have massive impacts on land and natural ecosystems. To build wells, pipelines, processing plants and waste disposal sites, entire portions of land are damaged dramatically.
Water Pollution
The extraction and treatment of fossil fuels represent a significant threat to water resources.
Other than the risk of water contamination, the production of fossil fuels consumes massive amounts of water. These keep on growing as drills extend and basins are overexploited.
Ocean Acidification
Seas and oceans absorb part of the carbon emissions generated by human activities. As a result, the water’s chemistry is altered, and acidity levels increase.
According to the Natural Resources Defense Council (2022), oceans have become 30% more acidic since the start of the Industrial Revolution.
The phenomenon of ocean acidification affects marine ecosystems, wildlife and coastal communities.
Public Health
According to a Harvard Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment study (2021), burning fossil fuels is responsible for about 1 in 5 deaths worldwide due to the hazardous air pollutants released.
The energy we need is right here. So why are we not using it?
Other than running out of time to halt climate change, we will run out of fossil fuels as well.
-png.png) Therefore, envisioning a green future and switching to renewable energy sources will be critical in the upcoming future.
Therefore, envisioning a green future and switching to renewable energy sources will be critical in the upcoming future.
Renewable energy sources, such as the sun, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal, are largely available and 'clean'.
According to the United Nations (n.d.), renewables are currently cheaper in most countries and generate three times more jobs than the fossil fuels industry.
-png.png)
Within the European Union, the EU Green Deal includes a plan for the decarbonisation of the EU’s energy system. To achieve the goal of making Europe climate neutral by 2050, the transition towards clean energy is pursued as follows:
- Ensure secure and affordable EU energy supply;
- Develop a fully integrated, interconnected and digitalised EU energy market;
- Prioritise energy efficiency and develop a power sector mainly based on renewable energy.
Additionally, the Just Transition Mechanism dedicates support to regions that will find it harder to move away from fossil fuels.
The Fund aims to mobilise at least €100 billion to:
- Finance the transition to low-carbon activities;
- Re-skill people employed in the non-renewable energy sector;
- Provide loans and easy access to financial support for all activities related to the green transition.
The EU Green Deal has also brought to life the EU Taxonomy. It consists of a tool to direct investments toward sustainable activities.
Renewable energy has a central role in the EU Taxonomy. Therefore, organisations shifting away from fossil fuels have higher chances of receiving support from banks and investors.
What can businesses do?
Despite the important role played by governments in the green energy transition, businesses also have a role to play.
To speed up the journey away from fossil fuels, organisations should:
Increase Energy Efficiency
You can reduce emissions generated by your operations while also cutting down costs. That sums up well the great benefits of improving the energy efficiency of your activities.
Moreover, improving energy efficiency has great potential to halt the climate crisis. As stated by ACEEE (2019), the USA could cut its energy use and GHG emissions in half by 2050 through improved energy efficiency.
Especially for organisations that are still heavily reliant on fossil fuels, reducing energy consumption is going to be key in the process of phasing out non-renewables.
Through a proper energy management system in place, organisations can track their energy consumption and optimise it.
Switch to Renewable Energy Sources
The best way to go when trying to curb the use of fossil fuels is to switch to renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy.
When purchasing renewable energy, make sure your providers are avoiding impacts on natural ecosystems and wildlife.
Green Power Purchase Agreements (Green PPAs) are a great tool to secure your access to reliable and certified clean energy over the medium and long term.
Additionally, organisations can cover part of their energy needs through on-site generation, for example by installing a solar panel system.
Invest in industrial electrification
According to McKinsey & Company (2020), almost 50% of fuel used for energy by industrial companies could be replaced with electricity using available technology.
The electrification of industrial production processes and fleets is gaining momentum thanks to lower costs of renewables and energy storage.
Conclusion

As we aim to decarbonise our economies and halt the climate crisis, moving away from fossil fuels becomes unavoidable.
It’s often said that challenges can turn into great opportunities, the green transition is already guaranteeing numerous advantages.
From reduced energy costs to reduced GHG emissions and widespread accessibility of renewable energy sources, we shouldn’t waste any more time (& energy) on the fossil fuels industry.